Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern in modern medicine. It refers to the ability of bacteria to resist the effects of antibiotics, which are used to treat bacterial infections. When bacteria become resistant to antibiotics, it can be difficult or impossible to treat infections caused by those bacteria. This can lead to longer hospital stays, higher healthcare costs, and in some cases, death. The misuse and overuse of antibiotics are the main causes of antibiotic resistance. When antibiotics are used too often or for non-bacterial infections, they can kill off the good bacteria in the body. This can lead to the growth of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which can then spread to others. One of the biggest challenges with antibiotic resistance is that it can happen quickly. Bacteria can mutate and develop resistance to antibiotics within a short period. This means that new antibiotics need to be developed constantly to keep up with the evolving bacteria. The consequences of antibiotic resistance are significant. Infections that were once easily treated with antibiotics can become life-threatening. Patients may need to be hospitalized for longer periods, and they may need more aggressive treatment to fight off the infection. In some cases, there may be no effective treatment available for antibiotic-resistant infections. Preventing antibiotic resistance is everyone’s responsibility. Patients can help by taking antibiotics only when they are needed and as prescribed by their healthcare provider. They should never save antibiotics for future use or share them with others. Healthcare providers can help by prescribing antibiotics only when necessary and using the appropriate type and dosage. They should also educate patients on the proper use of antibiotics. In addition to these steps, other actions are being taken to combat antibiotic resistance. Researchers are working to develop new antibiotics and alternative treatments such as phage therapy and probiotics. Governments are implementing policies to regulate the use of antibiotics in agriculture and livestock farming, which can contribute to the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The World Health Organization (WHO) has also launched a global action plan to address antibiotic resistance. One of the key components of the WHO’s action plan is to improve surveillance and data collection on antibiotic resistance. This will help identify trends and patterns in antibiotic resistance and guide the development of new treatments. The plan also calls for more research on the development of new antibiotics and alternative treatments. Antibiotic resistance is a complex issue that requires a multi-faceted approach. Individuals, healthcare providers, researchers, and policymakers need to work together to prevent the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. By taking action now, we can help ensure that antibiotics remain effective in treating bacterial infections for generations to come.
iSpeech.org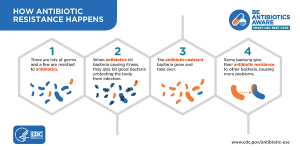
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE












Recent Comments